
Within their endogenous niche stem cells proliferate and differentiate always in a three-dimensional environment. However, most concepts of cell differentiation or short-time expansion of stem cells are applied as two-dimensional cultivation strategies Notably, 2D culture of stem cells is known to result in unnatural polarity and morphology as well as to induce an altered migration and differentiation capability of the given cell. Thus, there is a high need of 3D cell culture approaches, which more closely resemble the original niche of the stem cell.
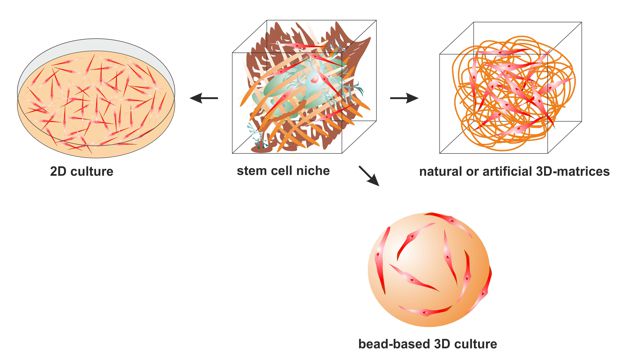
Fig. 1. 3D-cultivation approaches. After isolation out of their niche, stem cells can be either cultivated as a conventional 2D monolayer or grown on the surface of semisolid beads or embedded within a natural or artificial 3D matrix.
We are interested in the development of novel 3D cell culture protocols allowing rapid expansion of various stem cell populations in an animal component-free environment, without affecting their intrinsic properties. Our focus lies in 3D cultivation of mesenchymal, neural and neural crest-derived stem cells.
References
Greiner JF, Hauser S, Widera D, Müller J, Qunneis F, Zander C, Martin I, Mallah J, Schuetzmann D, Prante C, Schwarze H, Prohaska W, Beyer A, Rott K, Hütten A, Gölzhäuser A, Sudhoff H, Kaltschmidt C, Kaltschmidt B. Efficient animal-serum free 3D cultivation method for adult human neural crest-derived stem cell therapeutics.
Eur Cell Mater. 2011 Dec 17;22:403-19.
Greiner JF, Grunwald LM, Müller J, Sudhoff H, Widera D, Kaltschmidt C, Kaltschmidt B. Culture bag systems for clinical applications of adult human neural crest-derived stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2014 Mar 14;5(2):34. doi: 10.1186/scrt422.
Nguyen TD, Widera D, Greiner J, Müller J, Martin I, Slotta C, Hauser S, Kaltschmidt C, Kaltschmidt B. Prolonged cultivation of hippocampal neural precursor cells shifts their differentiation potential and selects for aneuploid cells.
Biol Chem. 2013 Dec;394(12):1623-36. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2013-0191.
Greiner JF, Kaltschmidt B, Kaltschmidt C, Widera D. Going 3D – Cell Culture Approaches for Stem Cell Research and Therapy. Current Tissue Engineering, 2013, 2, 8-19
Schwann cells (SCs) are supporting cells of the peripheral nervous system and were first described by Theodor Schwann in 1839. In general, SCs can be classified in myelinating and non-myelinating SCs. They provide trophic and structural support of peripheral neurons and play a pivotal role in regeneration after injury. Recent reports suggest that in response to injury or infection (e.g. with Leprosy Bacilli) they dedifferntiate into plastic NCSC-like state allowing them to generate neurons, glial and mesenchymal cell types.
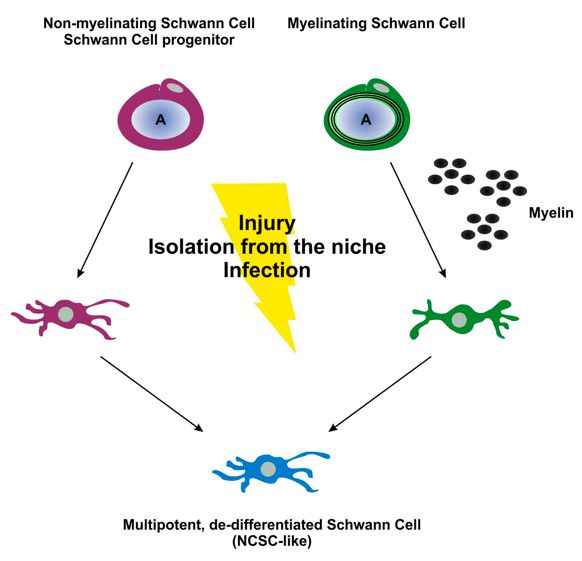
Fig. 1 Both - myelinating and non-myelinating Schwann cells can be reprogrammed towards a neural crest stem cell-like phenotype by lesion of removal of their niche (injury mimicry).
We were able to show that mouse and rat derived myelinating and non-myelinating SCs are able to acquire NCSCs-like phenotype after removal from their niche and in vitro cultivation under appropriate conditions.
Currently, we want to understand how the process of dedifferentiation is regulated at molecular level. Importantly, a deep understanding of the cellular reprogramming of SCs will provide the option to use this cell type as a novel, ethically unquestionable stem-like cell type for treatment of degenerative disorders in humans.
References
Martin I, Nguyen TD, Krell V, Greiner JF, Müller J, Hauser S, Heimann P, Widera D. Generation of Schwann cell-derived multipotent neurospheres isolated from intact sciatic nerve. Stem Cell Rev. 2012 Dec;8(4):1178-87. doi: 10.1007/s12015-012-9387-2.
Widera D, Heimann P, Zander C, Imielski Y, Heidbreder M, Heilemann M, Kaltschmidt C, Kaltschmidt B. Schwann cells can be reprogrammed to multipotency by culture. Stem Cells Dev. 2011 Dec;20(12):2053-64. doi: 10.1089/scd.2010.0525. Epub 2011 Jun 1.
Widera D, Hauser S, Kaltschmidt C, Kaltschmidt B.Origin and regenerative potential of vertebrate mechanoreceptor-associated stem cells. Anat Res Int. 2012;2012:837626. doi: 10.1155/2012/837626. Epub 2012 Oct 2.
Adult stem cells are tissue resident and thus affected by local injury, infection and inflammation. However, the impact of pro- and anti-inflammatory signalling on stem cells is not fully understood. In particular, inflammation seems to have different effects on proliferation, differentiation and migration of stem cells depending on the origin of the cell (tissue and species), the developmental context (embryonic vs adult) and the duration of the exposure to the signal (acute vs. chronic inflammation).
Here, we are mainly interested in the signalling cascaded mediated by the Toll-like Receptor 4 (TLR4) and Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor 1 (TNF-R1). Notably, while stimulation of TNF-R1 leads to activation of pro-inflammatory signalling, ligation of TLR4 culminates in both: pro- and anti-inflammatory signal transduction.
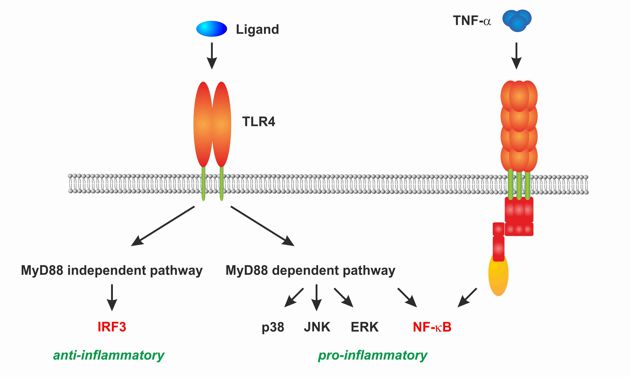
Fig. 1. Activation of TLR4 can culminate in pro- and anti-inflammatory signalling. In contrast, binding of Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha to TNF-R1 exclusively activates pro-inflammatory signalling mainly mediated by the transcription factor NF-kappaB.
We want to understand how the inflammatory balance and manipulation thereof influences differentiation, proliferation and migration of stem cells, including neural stem cells, mesenchymal stem cells and neural crest-derived stem cells. We use modern microscopy in addition to biochemical methods to understand the respective signal transduction pathways at the level of receptors and the downstream signalling events.
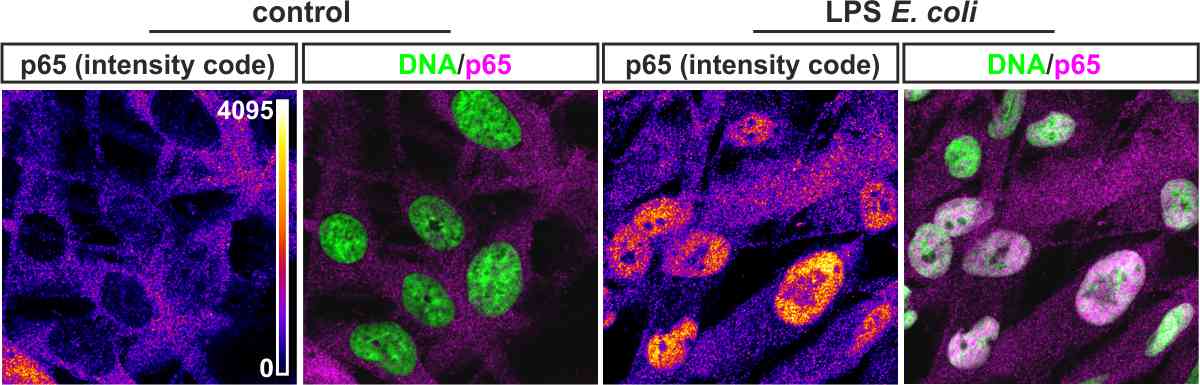
Fig. 2. Treatment of U251 model cell line with the TLR4-ligand LPS leads to nuclear translocation of the pro-inflammatory transcription factor NF-kappaB as visualized using antibodies against its subunit p65.
Our work on TLR4 is a collaboration with Prof. Mike Heilemann (Institute for Physical and Theoretical Chemistry Goethe-University Frankfurt, Germany) and is funded by the German Research Council DFG (WI4318/2-1).
References
Zeuner M, Bieback K, Widera D. Controversial Role of Toll-like Receptor 4 in Adult Stem Cells.Stem Cell Rev. 2015 Aug;11(4):621-34. doi: 10.1007/s12015-015-9589-5.
Fricke F, Malkusch S, Wangorsch G, Greiner JF, Kaltschmidt B, Kaltschmidt C, Widera D, Dandekar T, Heilemann M.Quantitative single-molecule localization microscopy combined with rule-based modeling reveals ligand-induced TNF-R1 reorganization toward higher-order oligomers. Histochem Cell Biol. 2014 Jul;142(1):91-101. doi: 10.1007/s00418-014-1195-0. Epub 2014 Feb 12.
Heidbreder M, Zander C, Malkusch S, Widera D, Kaltschmidt B, Kaltschmidt C, Nair D, Choquet D, Sibarita JB, Heilemann M.TNF-α influences the lateral dynamics of TNF receptor I in living cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Oct;1823(10):1984-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2012.06.026. Epub 2012 Jun 27.
Heidbreder M, Endesfelder U, van de Linde S, Hennig S, Widera D, Kaltschmidt B, Kaltschmidt C, Heilemann M. Subdiffraction fluorescence imaging of biomolecular structure and distributions with quantum dots. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010 Oct;1803(10):1224-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2010.06.004. Epub 2010 Jun 23.
Widera D, Kaus A, Kaltschmidt C, Kaltschmidt B. Neural stem cells, inflammation and NF-kappaB: basic principle of maintenance and repair or origin of brain tumours? J Cell Mol Med. 2008 Apr;12(2):459-70. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2007.00208.x. Epub 2007 Dec 20.
Widera D, Mikenberg I, Elvers M, Kaltschmidt C, Kaltschmidt B. Tumor necrosis factor alpha triggers proliferation of adult neural stem cells via IKK/NF-kappaB signaling. BMC Neurosci. 2006 Sep 20;7:64.
Post- and undergraduate projects conducted under full/partial supervision of Dr Widera (first or second supervisor)
Kat Cottingham - "Generating Cardiomyocytes from Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells: a Study of Differentiation Protocol Optimisation", MRes thesis, 2016, University of Reading, UK
Liam Turner - "TNF-alpha activates NF-kappaB and induces apoptosis in neural crest-derived stem cells", MRes thesis, 2016, University of Reading, UK
Thomas Fitzgerald - "The Clinical and Therapeutic Potential of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes", MPharm dissertation, 2016, University of Reading, UK
Grant Mehrjou - "Exploring the Therapeutic Potential of Olfactory Ensheathing Cells and Schwann Cells in Spinal Cord Injuries", MPharm dissertation, 2016, University of Reading, UK
Sofiat Hameed - "Effectiveness of Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSC) In Heart Failure; A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis", MPharm dissertation, 2016, University of Reading, UK
Matthias Bolowski - "Influence of conserved signals on recycling of a defined synaptic vesicle population", external MSc thesis, 2014, European Neuroscience Institute, Göttingen, Germany
Ines Schlotböller - "Consequences of TLR4-ligation on proliferation and differentiation of various astroglioma cell lines", BSc thesis, 2014, University of Bielefeld, Germany
Marie-Theres Zeuner - "Potential role of 1,8-cineol for treating viral infection in human cell lines and nasal turbinate slices", MSc thesis, 2014, University of Bielefeld
Katharina Volk – „Impact of different ligands on TLR4-mediated signal transduction“, MSc thesis, 2014, University of Bielefeld, Germany
Lena-Marie Grunwald – “The impact of 1.8 cineol in human stem cells and cell lines”, MSc thesis, 2013, University of Bielefeld, Germany
Frederique Wieters, „Influence of different lipopolysaccharides on TLR4 in U373 cells", BSc thesis, 2013, University of Bielefeld, Germany
Gina Marlene Cheung – „Recombinant expression of T7 RNA polymerase in E.coli for amplification of RNA from single mammalian cells”, BSc thesis, 2013, University of Bielefeld, Germany
Jennifer Chudzienski – „Investigation of TLR4-mediated signaling in U251 astroglioma cell line“, BSc thesis, 2013, University of Bielefeld, Germany
Timo Schomann, "In vivo differentiation potential of ITSCs in the developing chicken embryo model", MSc thesis, 2013, University of Bielefeld, Germany
Marie-Theres Zeuner, „Effects of 1,8-cineol on NF-kappaB signaling pathway in human cells ex vivo", BSc thesis, 2012, University of Bielefeld, Germany
Daniela Drüke, „Novel Strategies of Dopaminergic Differentiation of Adult Human Neural Crest-derived Stem Cells: Molecular Cloning of MicroRNA-constructs Potentially Inducing Dopaminergic Programming”, BSc thesis, 2012, University of Bielefeld, Germany
Sebastian Korste, „Integration and differentiation of adult human neural-crest derived stem cells in organotypic hippocampal slices“,BSc thesis, 2012, University of Bielefeld, Germany
The Duy Ngyuen, "In vitro differentiation potential of hippocampal progenitors and generation of Schwann cell.derived neurospheres from mus musculus", MSc thesis, 2012, University of Bielefeld, Germany
Ina Martin, „Investigation on the differentiation potential of adult hippocampal progenitors and reprogrammed Schwann cells: potential role of NF-kappaB”, MSc thesis, 2012, University of Bielefeld, Germany
Johannes Greiner, „Flow cytometric characterisation and novel animal-serum free cultivation of neural crest-derived human inferior turbinate stem cells“, MSc thesis, 2012, University of Bielefeld, Germany
Janine Müller, „Identification of novel human neural crest-derived stem cells within adult concha nasalis inferior“, MSc thesis, 2012, University of Bielefeld, Germany
Verena Gawrisch, "Investigation of the potential role of Hsc70 and Hsp90 in the retrograde transport of KF-kappaB", MSc thesis, 2011, University of Bielefeld, Germany
Timo Schomann, „Influence of pluripotency genes Nanog, Sox2 and Oct4 on NF-kappaB“, BSc thesis, 2011, University of Bielefeld, Germany
Anna Marie Walter, "Identification of novel PKA phosphorylation targets by MALDI-TOF/TOF”, MSc thesis, 2011, University of Bielefeld, Germany
Tim Salbert, "Molecular cloning of split-YFP constructs for investigation of interactions between HSPA8, HSP90 and NF-kappaB", BSc thesis, 2010, University of Bielefeld, Germany
Stefan Hauser, "Characterization of novel human adult neural crest-derived stem cells", MSc thesis, 2010, University of Bielefeld, Germany
Firas Qunneis, "Expression, purification and functional testing of recombinant human basic growth factor bFGF (FGF-2)", MSc thesis, 2010, University of Bielefeld, Germany
Christin Zander, "Bioinformatic characterization of plant Ikappab kinase-homologues", MSc thesis, 2008, University of Bielefeld, Germany
Michael, Könnecke, "Research into cloning of plant IKK-like proteins”, MSc thesis, 2008, University of Bielefeld, Germany
Carolin Haubenreich, "Reprogramming and growth of adult neural stem cells", MSc thesis, 2008, University of Bielefeld, Germany
Meike Heidbreder, "Characterisation of neural crest stem cells from various cellular sources", MSc thesis, 2008, University of Bielefeld, Germany
Clara Beutner, "Analysis of the role of transcription factor NF-kappaB in neural crest-derived stem cells", MSc thesis, 2008, University of Bielefeld, Germany

