
Prof Karen Bieback, University of Heidelberg, Germany
Dr Graeme Cottrell, University of Reading, UK
Dr Mark Dallas, University of Reading, UK
Dr Bernd Denecke, Chip Facility, RWTH Aachen, Germany
Prof Anastasia Efimenko, Lomonosov Moscow State University, Russia, (on hold since 24/02/2022)
Dr Bernd Giebel, University Hospital Essen, Essen, Germany
Prof Wolf-Dieter Grimm, Witten/Herdecke University
Prof Sema Hakki, Selcuk University, Konya, Turkey
Prof Mike Heilemann, Johann Wolfgang Goethe-University, Frankfurt a.M., Germany
Prof Barbara Kaltschmidt, University of Bielefeld, Bielefeld, Germany
Prof Christian Kaltschmidt, University of Bielefeld, Bielefeld, Germany
Dr Patrick Lewis, University of Reading, UK
Dr Wee Kiat Ong, University of Reading Malaysia, Johor Bahru, Malaysia
Prof Helen Osborn, University of Reading, UK
Prof Roisin Owens, Cambridge, UK
Prof Ketan Patel, University of Reading, UK
Dr Selvee Ramasamy, University of Malaya, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
Prof Shigeki Sugii, A*STAR, Singapore
Prof Evgenii Skurikhin, Research Institute of Pharmacology and Regenerative Medicine, Tomsk, Russian Federation (on hold since 24/02/2022)
Dr Sakthihivel Vaiyapuri, University of Reading, UK
Prof Badrul Yahaya, Universiti Sains Malaysia, Penang, Malaysia
The Hopkins Building is located on the Whiteknights Campus of the University of Reading (lower right corner of the map, building 118)

Hopkins building, Whiteknights campus.
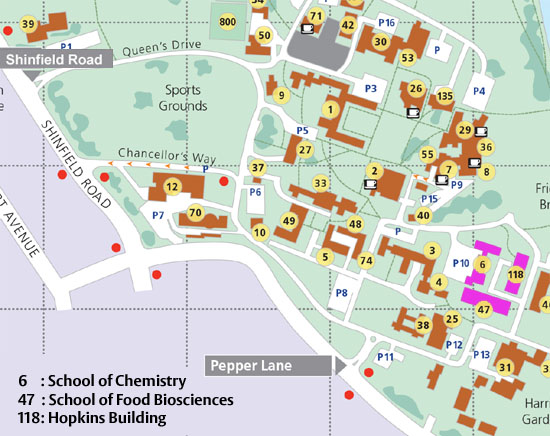
A map on how to reach Reading, can be found on Google maps.
Please note: If you are using a 'sat nav' or 'GPS' navigation system such as a 'Tom Tom', please use the following postcode in order to navigate to Whiteknights Campus: RG6 6UR
The Neural Crest (NC) is a transient embryonic structure which appears between the Neural Chord and the future ectoderm during development of the vertebrate embryo. NC cells migrate out of their niche after neurulation and give rise to various cell populations. Importantly, especially in the cranial region, NC cells differentiate not only into ectodermal derivatives such as peripheral neurons and melanocytes, but are also able to generate mesenchymal progeny (e.g. osteoblasts) (see Fig 1).
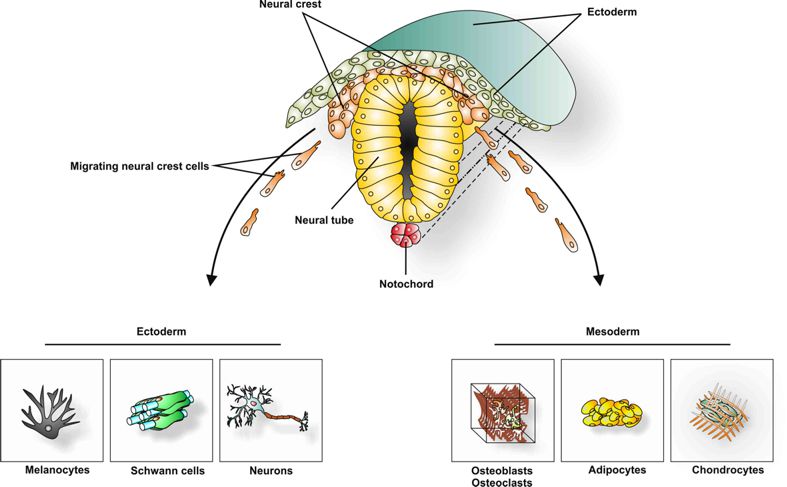
Fig. 1. Derivatives of cranial NC cells.
In past, we successfully identified NC-derived stem cells (NCSCs) within different rodent and human tissues such as the periodontal ligament, palate or nasal tissue (inferior turbinate). Main advantages of such adult NCSCs are their easy accessibility and high plasticity without being ethically questionable.
We are interested in novel sources of NCSCs and their regenerative potential in different experimental and pathological scenarios including disease and injury models.
References
Weber M, Apostolova D, Widera D, Mittelbronn M, Dechant G, Kaltschmidt B and Rohrer H. Alternative generation of CNS neural stem cells and PNS derivatives from neural crest derived peripheral stem cells
Stem Cells. 2015 Feb;33(2):574-88. doi: 10.1002/stem.1880.
Müller J, Ossig C, Greiner J, Hauser S, Fauser M, Widera D, Kaltschmidt C, Storch A and Kaltschmidt B. Intrastriatal transplantation of adult human neural crest-derived stem cells improves functional outcome in Parkinsonian rats. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2015 Jan;4(1):31-43. doi: 10.5966/sctm.2014-0078.
Schürmann M, Wolff A, Widera D, Hauser S, Heimann P, Hütten A, Kaltschmidt C and Kaltschmidt B. Interaction of adult human neural crest-derived stem cells with nanoporous titanium surface is sufficient to induce their osteogenic differentiation. Stem Cell Res. 2014 May 9;13(1):98-110. doi: 10.1016/j.scr.2014.04.017. [Epub ahead of print]
Kaltschmidt B, Kaltschmidt C, Widera D. Adult craniofacial stem cells: sources and relation to the neural crest. Stem Cell Rev. 2012 Sep;8(3):658-71. doi: 10.1007/s12015-011-9340-9.
Hauser S, Widera D, Qunneis F, Müller J, Zander C, Greiner J, Strauss C, Lüningschrör P, Heimann P, Schwarze H, Ebmeyer J, Sudhoff H, Araúzo-Bravo MJ, Greber B, Zaehres H, Schöler H, Kaltschmidt C, Kaltschmidt B. Isolation of novel multipotent neural crest-derived stem cells from adult human inferior turbinate. Stem Cells Dev. 2012 Mar 20;21(5):742-56. doi: 10.1089/scd.2011.0419. Epub 2012 Jan 26.
Widera D, Zander C, Heidbreder M, Kasperek Y, Noll T, Seitz O, Saldamli B, Sudhoff H, Sader R, Kaltschmidt C, Kaltschmidt B. Adult palatum as a novel source of neural crest-related stem cells. Stem Cells. 2009 Aug;27(8):1899-910. doi: 10.1002/stem.104.
Widera D, Grimm WD, Moebius JM, Mikenberg I, Piechaczek C, Gassmann G, Wolff NA, Thévenod F, Kaltschmidt C, Kaltschmidt B.Highly efficient neural differentiation of human somatic stem cells, isolated by minimally invasive periodontal surgery. Stem Cells Dev. 2007 Jun;16(3):447-60.

